An Efficient Alternative for Modeling Spatial Prepositions with RDF Helper Nodes Based on the Environment Perception of a Mobile Robot
Today, thanks to the advancement of robotics and intelligent new technologies, robots are entering more and more into different areas of human life. In doing so, the interaction between humans and robots, involving solving tasks both supervised and collaborative, becomes increasingly important as they both rely on smart approaches for communication.
Throughout the human-robot and robot-robot communication, the utilized technology has to be able to describe information that is semantically rich, structurally efficient concerning description and time efficient regarding the retrieval of information.
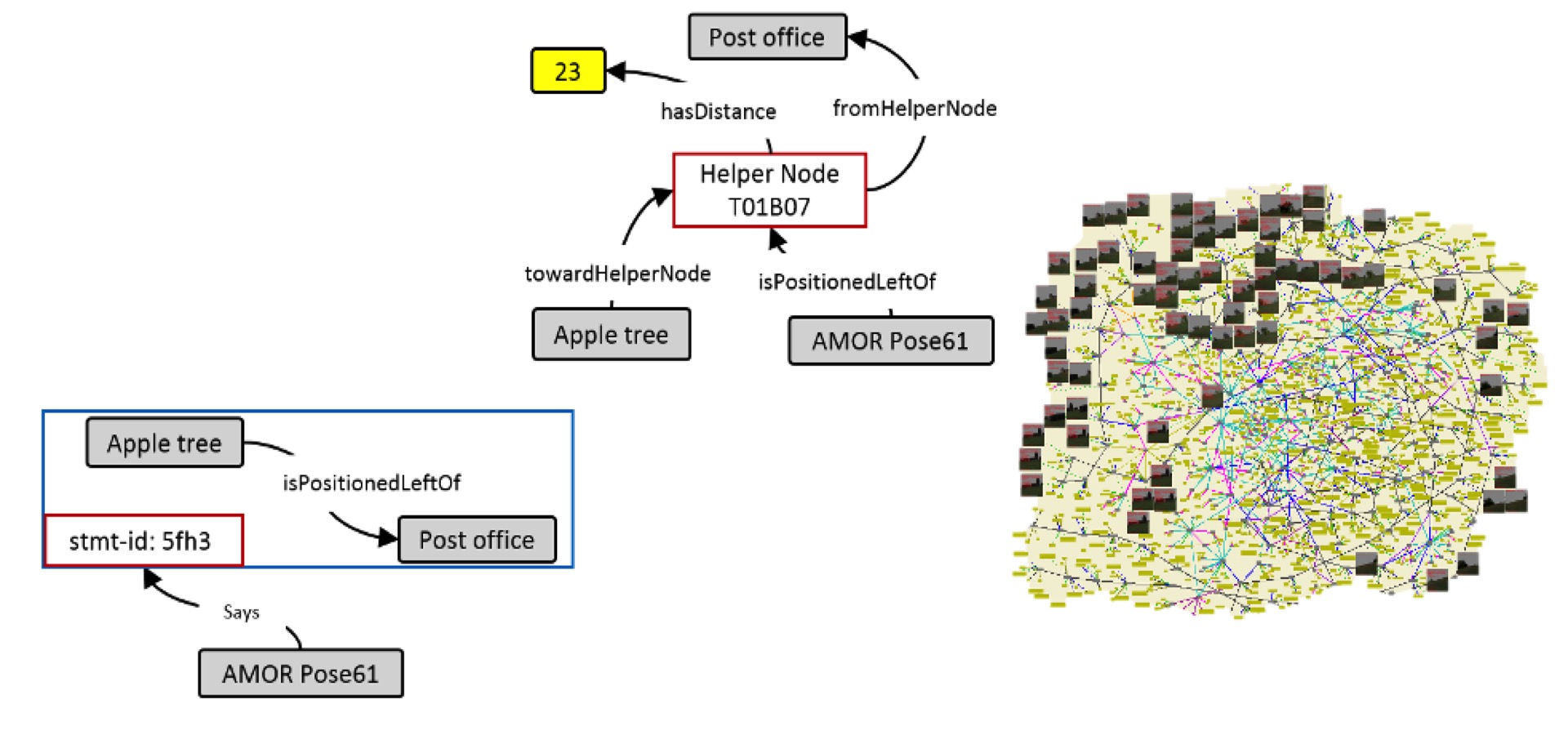
This work utilizes the resource description framework (RDF), as one of the core technologies of the semantic web to describe the navigation of a mobile robot semantically in an ontology which is populated in real-time.
This research proposes a new and efficient way of expressing semantic relationships within the navigation ontology by using helper nodes. In contrast to existing approaches, it could be shown that the use of helper nodes can cut down the generation of nodes by a factor of two, improving the storage but also the utilization for a time efficient communication.
