An Approach for Modeling Spatial Prepositions with RDF Reification and Blank Nodes Based on the Environment Perception of a Simulated Mobile Robot
Today, thanks to the advancement of robotics and the achievements that are made in the light of the development of automated and intelligent technologies, we are increasingly witnessing the arrival of robotic devices and machines into different areas of human life. With all of the achievements and their intelligence, the degree of their proficiency relies in many cases on their ability to interact with human beings.
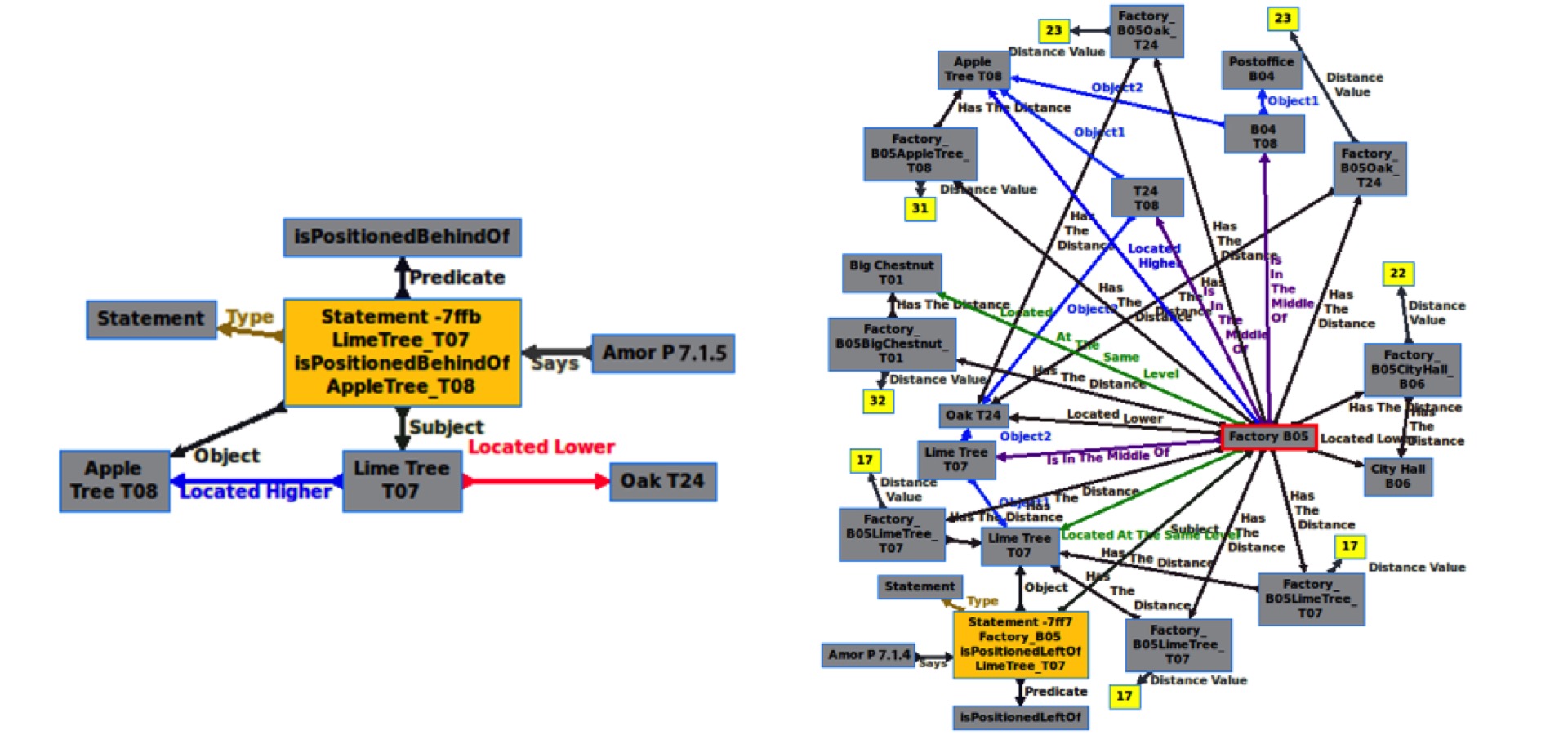
To do so, for a mobile robot the ability to understand its surroundings and also to describe it in a way that human can easily understand is vitally important. “Above”, “below”, “in front of”, “behind of”, “left of” and “right to” are prepositions that human uses in daily life to describe not only the relationship between objects but also to provide one's location implicitly.
The Resource Description Framework, RDF, as one of the semantic web core components, can be employed for forming those prepositions. The idea is to utilize a smart sensor of a simulated, mobile robot for creating semantic information in RDF format that represents inter-object relations by using the same spatial prepositions that human uses in his daily life to describe his environment.
